WAN (Wide Area Network) Settings
Once we have signed up to an ISP that can provide a static public IP address, they will provide the following IP details.
- Gateway
- Static public IP
- Subnet mask
- Primary DNS address
- Secondary DNS address
Log into your router and enter the above information. If you have not logged into your router before, you will need to open a web browser and enter the routers IP address into the web browsers address bar. The router IP address is usually on the back of the router (192.168.1.1 for example), possibly with the default username and password. If you can’t find the password you will need to do a search for the default password of your routers model number.
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is a mechanism where the router listens for incoming connections on a certain port and forwards that connection to a given private IP, in our case the server. We are using L2TP so the router needs to listen to port 500, 1701, and 4500, using the UDP protocol, with the servers private IP as the internal IP address. You will need to consult your routers documentation on how to do this. The example below shows the process for the ASUS RT-AC68U router.
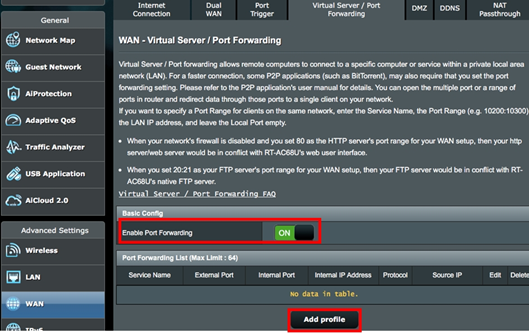
- Open your browser, type in http://router.asus.com and go to “Advanced Settings”.
- Click on “WAN,” and choose “Virtual Server / Port Forwarding.”
- Select on “Enable Port Forwarding,” and click on “Add profile.”
- From the “Famous Server List” select “L2TP / IPSec VPN Server”. This will auto populate the fields using the internal IP address from the server.
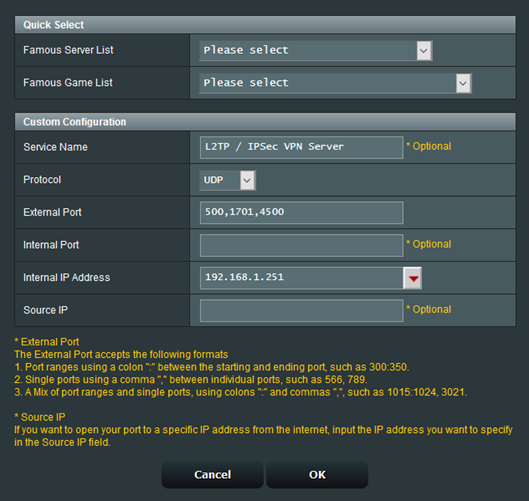
- Click OK. You are now finished with the router.